InSitupedia
Variants
There are different categories of ISH methods:
ISH started being performed using radioisotope labeling.
Because of the safety measures required, the short life of the isotopic probes and the extensive time required for exposure to autoradiography (it was needed 1 week for the best probes), this method become out of use.
Even so, the radioactive hybridization is still used because this method allows further detection sensitivity of low abundance transcripts and quantitative analyses, provides a long-term record of target gene expression and does not require multiple amplification steps.
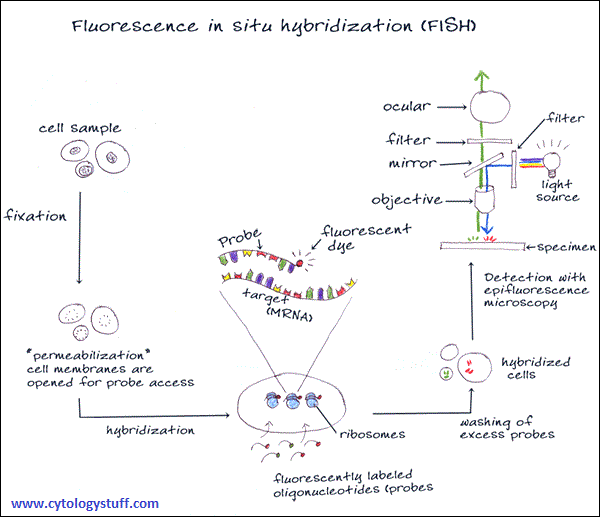
Nonisotopic ISH methods are mostly used nowadays due to the greater stability of probes, rapid results and better resolution.
The detectable molecule (reporter) is bound directly to the nucleic acid probe so that probe-target hybrids can be visualized under a microscope immediately after the hybridization reaction. It is used fluorescein or other fluorochromes directly coupled to the nucleotide.
The hybridization signals can be detected by addition of an antidigoxigenin antibody conjugated to AP, HPO + substrates that yield insoluble-colored products.
Less sensitive than the radioactive probes, the hybridization results are more difficult to quantify.